3.3: How to Reference Karamba3D Assemblies
In order to package the script of section 2.4.2 into a GH-component there needs to be one input-plug that receives a Karamba3D model. Three output plugs return an updated Karamba3D model, a list of boolean values that signifies which elements are active or not and the value of the largest resultant displacement.
The following example can be found in the examples that accompany this guide. Go to “#/TensionElim” and double-click on “TensionElim.sln” to open the project with Visual Studio. Depending on what version of Grasshopper you use it will be necessary to reestablish the project references.
Referencing Required Libraries: To use Karamba3D classes (e.g., the Model class), you must reference the karambaCommon.dll library. There are two ways to do this:
Using the KarambaCommon NuGet Package:
In Visual Studio, go to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solution... and install the
KarambaCommonpackage.
Referencing the Installed Library:
Right-click References in the Solution Explorer and select Add Reference....
In the tabbed view, go to Browse and locate the
karambaCommon.dllfile in Rhino’s Plug-ins folder.
Including karamba.gha: Since Karamba3D will be used in Grasshopper, you must also reference karamba.gha. However, Visual Studio does not natively allow .gha files to be selected. Use the following workaround:
Save and close your Visual Studio project.
In the project directory, locate the
TensionElim.csprojfile and open it in a text editor.Search for the
karambaCommonentry, copy it, and modify it to referencekaramba.gha(see Fig. 3.3.1 in the guide).Save the file and reopen the project in Visual Studio.
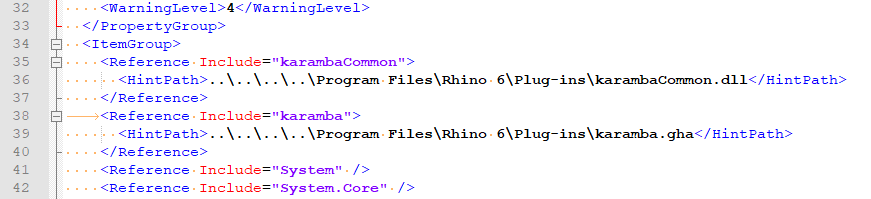
Adjusting Reference Properties:
After adding
karambaandkarambaCommonreferences, right-click each reference in Solution Explorer and select Properties.Set the Copy Local property (default:
True) toFalse.
Following these steps ensures the script is properly packaged into a custom Grasshopper component for use with Karamba3D.
Last updated