2.1: Hello Karamba3D
For small scripts the Grasshopper scripting components “C# Script”, “VB Script” or “Python Script” from the “Maths” subsection come in handy. A good introduction to scripting in GH can be found in the “Grasshopper Primer”.
All examples which follow can be found in the “Karamba3D Scripting Examples Github”-collection that accompanies this manual. When opening them in Grasshopper do not panic if some components turn red. In that case some paths need adaptation (see below).
Setting up a Script in Rhino6/7
To begin using Karamba3D in a Grasshopper script, follow this example (refer to “HelloKaramba3D_RH7.gh” linked at the bottom of the relevant documentation page):
Add a C# Scripting Component
Place a C# scripting component onto the Grasshopper canvas.
Manage Assemblies
Right-click on the component's icon and select "Manage Assemblies..." from the context menu.
Add Karamba3D Assemblies
Under "Referenced Assemblies," click "Add."
Browse to locate the
karambaCommon.dllandkaramba.ghafiles. These files are typically located in the Rhino Plug-ins folder:C:\Program Files\Rhino7\Plug-ins\Karamba3DEnsure you select the appropriate file type:
By default, only
.dllfiles are visible.Use the drop-down menu in the lower-right corner of the file browser to select "Grasshopper Assemblies (*.gha)" for the
.ghafile.
This setup makes the Karamba3D assemblies accessible to your script, enabling full integration with the plug-in.
Setting up a Script in Rhino8
The Rhino 8 script editor for C# introduces significant improvements over its predecessor, including built-in debug support. To reference external assemblies, you can explicitly include them in your code.
Adding Karamba3D Assemblies
For example, the following lines reference the required Karamba3D assemblies (see "HelloKaramba3D_RH8.gh" at the bottom of this page):
Replace
<YourUsername>with your specific user name to match your installation path.The files are located in the personal folder if Karamba3D was installed via the YAK package manager.
Convenient Assembly Selection
For a more user-friendly approach to referencing assemblies:
Use the "Box" button in the script editor toolbar to open the assembly selection browser.
Browse and add the required files directly.
By following these steps, you can integrate Karamba3D assemblies into your Rhino 8 C# scripts with ease.
Explanation of Code
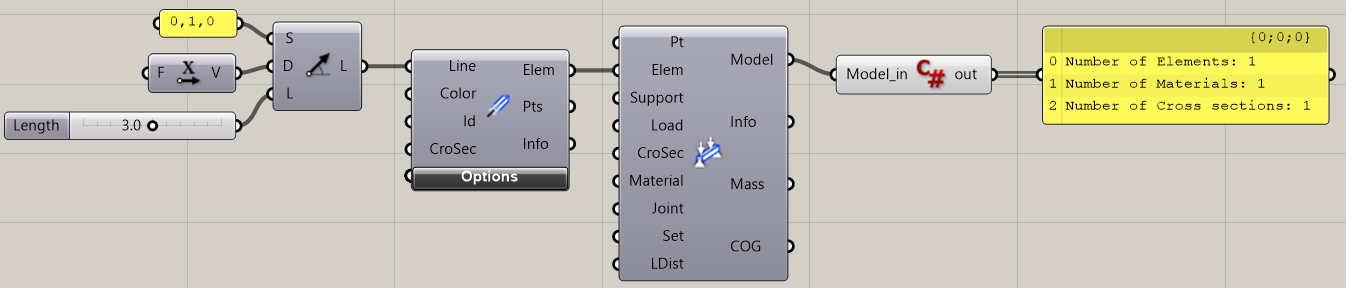
The source-code to be added inside the C#-component looks like this:
Namespace Inclusion: The
usingdirective (using Karamba.Models;) allows shorter, more readable code. For example, instead of typingKaramba.Models.Model, you can simply useModel.Casting the Input:
Model_inis provided as anobject.To access its properties, it must be cast to the correct type (
Model).The
ifcondition checks if the casting was successful. If not, anArgumentExceptionis thrown to handle invalid inputs (e.g., a vector plugged into the model input).
Accessing the Model:
Once cast, the
modelvariable holds a reference to the Karamba3D model.The script retrieves data about the model, such as the count of elements, materials, and cross-sections.
Output Details:
Use
Printto display the results in the Grasshopper console.Example outputs:
Number of Elements: 1
Number of Materials: 1
Number of Cross sections: 1
API Documentation
For detailed information about the Model class and its API, visit the Karamba3D API Documentation, specifically under Karamba.Models.
Last updated